Self-Supervised Learning for SAR Target Recognition with Multi-Task Pretext Training
We developed a self-supervised learning framework for Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Automatic Target Recognition that eliminates dependency on synthetic data while achieving superior performance. Our framework utilizes multi-task pretext training with nine complementary transformation tasks to develop robust feature representations from measured SAR data. The experimental findings demonstrate competitive performance with 89.78% accuracy using SVM classifier and robust detection capabilities even with limited training data, outperforming traditional methods that rely on synthetic data augmentation. This work establishes a foundation for leveraging self-supervised learning in domain-specific applications with limited labeled data.
We developed a groundbreaking self-supervised learning framework for Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Automatic Target Recognition (ATR) that eliminates the dependency on synthetic data while achieving superior performance. This research addresses critical limitations in SAR target recognition by leveraging multi-task pretext training to learn robust feature representations directly from measured SAR data.
Research Problem Addressed
SAR Automatic Target Recognition faces two major obstacles:
- Scarcity of labeled data due to complex operational conditions
- Persistent domain gaps between synthetic and measured imagery that limit ATR performance
Our framework fundamentally eliminates the need for synthetic data augmentation while achieving state-of-the-art performance with significantly reduced training data requirements.
Our Approach
Unlike traditional methods that rely on synthetic data to bridge training gaps, our self-supervised learning framework learns robust representations directly from measured SAR data through innovative multi-task pretext training.
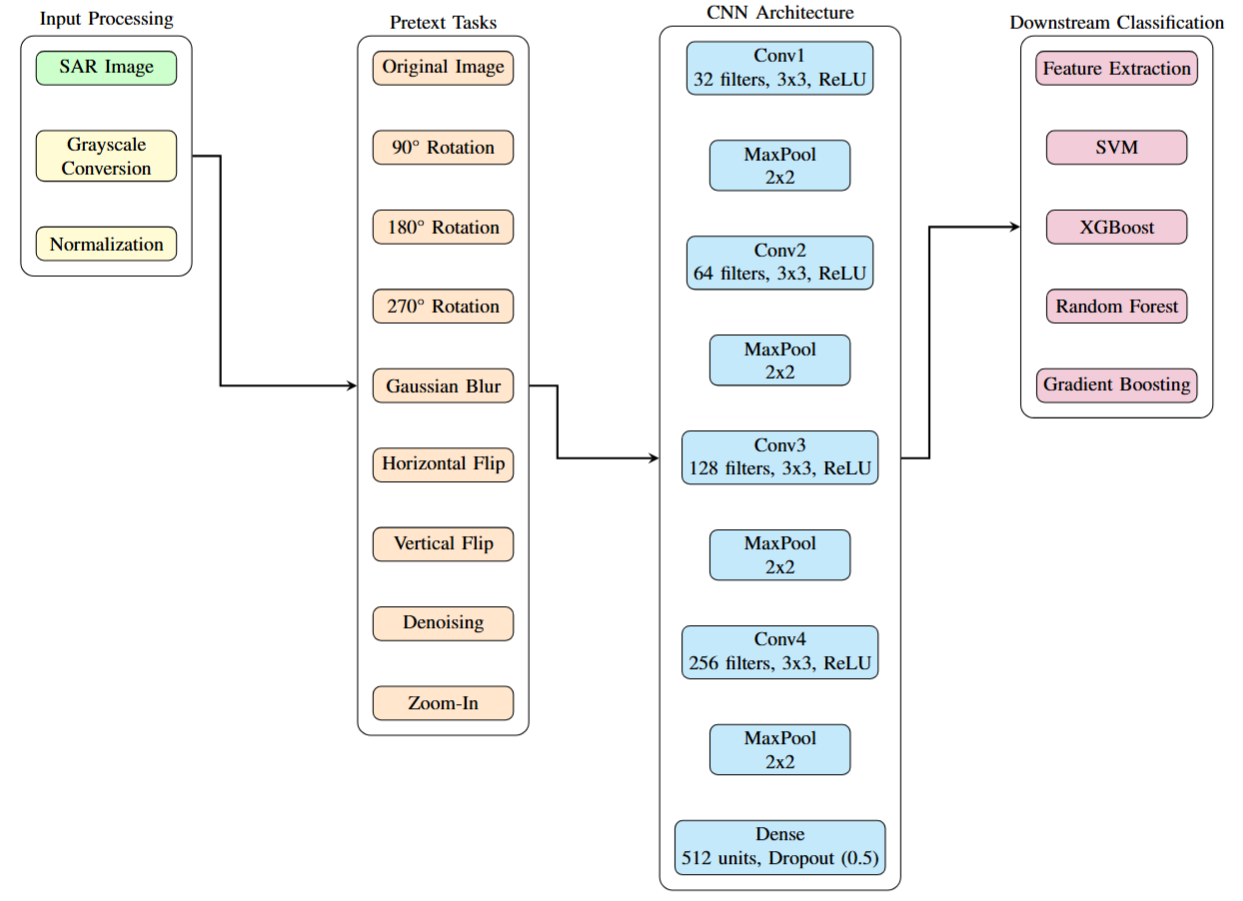
Multi-Task Pretext Training
Our framework employs nine complementary pretext tasks designed specifically for SAR data characteristics:
- Original Image Preservation - Maintains fundamental SAR signature characteristics
- Multi-Angle Rotation (90°, 180°, 270°) - Exploits viewpoint-invariant nature
- Gaussian Blur - Simulates varying resolution scenarios
- Horizontal/Vertical Flip - Learns geometric invariances
- Advanced Denoising - Handles inherent SAR speckle noise using BM3D algorithm
- Zoom-In Transformation - Enables multi-scale feature learning
Specialized CNN Architecture
- Four convolutional blocks (32, 64, 128, 256 filters)
- Batch normalization for training stability
- Strategic dropout (0.5) for robust generalization
- 512-unit dense embedding space for feature extraction
Experimental Validation


SAMPLE Dataset Evaluation
We extensively evaluated our framework on the Synthetic and Measured Paired and Labeled Experiment (SAMPLE) dataset containing:
- 10 distinct military vehicles
- 1,345 measured SAR images
- Multiple viewing angles (10° to 80° azimuth, 14° to 17° elevation)
Outstanding Results
Primary Framework Performance
- SVM Classifier: 89.78% average accuracy (best performing)
- XGBoost: 81.55% average accuracy
- Gradient Boosting: 80.89% average accuracy
- Random Forest: Competitive performance across all metrics
Exceptional Detection Capabilities
- 96.64% True Positive Rate at 5% False Positive Rate
- AUC Score: 0.9934 demonstrating excellent discriminative capability
- Robust performance even with 30% less training data
Lewis et al. Experimental Adaptation
Our SSL adaptation of the original Lewis et al. experiment achieved:
- 95.79% accuracy at k=0.90 (90% measured data)
- 99.52% TPR at 5% FPR
- Superior performance without any synthetic data dependency
- 99.09% accuracy with full measured data (outperforming original approach)
Key Technical Achievements
Synthetic Data Independence
- Eliminated reliance on synthetic SAR data completely
- Addressed domain gap issues that plague traditional approaches
- Direct learning from measured data preserves real-world phenomenology
Data Efficiency
- 68.4% of available measured data used for training (920 images total)
- Competitive performance with significantly reduced data requirements
- Robust generalization across diverse operational conditions
Multi-Classifier Validation
Comprehensive evaluation across multiple downstream classifiers:
- Support Vector Machine (Linear kernel)
- XGBoost (100 estimators)
- Random Forest (100 estimators)
- Gradient Boosting (100 estimators)
Real-World Applications



Military & Defense
- Autonomous target recognition for unmanned systems
- Real-time surveillance with minimal false alarms
- Multi-platform integration across various SAR sensors
- Battlefield intelligence with reliable target identification
Civilian Applications
- Maritime monitoring for ship detection and classification
- Infrastructure monitoring using satellite SAR data
- Environmental surveillance for change detection
- Disaster response with rapid target assessment
Research Significance
Academic Impact
- Novel SSL framework specifically designed for SAR domain
- Eliminates synthetic data dependency - a persistent challenge in SAR ATR
- Comprehensive evaluation methodology for domain-specific SSL
- Foundation for future research in radar-based computer vision
Technical Advancement
- Multi-task pretext learning adapted for SAR phenomenology
- State-of-the-art performance with reduced computational requirements
- Robust feature representations generalizing across operational conditions
- Practical deployment ready for real-world SAR systems
Future Research Directions
Enhanced SSL Techniques
- Additional domain-specific pretext tasks (frequency simulation, viewing angle modeling)
- Contrastive learning approaches for SAR data
- Multi-modal SSL incorporating radar and optical data
- Temporal sequence modeling for moving target recognition
System Integration
- Real-time processing optimization for operational systems
- Edge deployment for resource-constrained platforms
- Federated learning across distributed SAR networks
- Adversarial robustness for hostile environments
Technical Specifications
- Framework: TensorFlow/Keras with custom SSL pipeline
- Input Resolution: 128×128 grayscale SAR images
- Training Strategy: Multi-task pretext learning with 9 complementary tasks
- Feature Dimension: 512-dimensional embedding space
- Optimization: Adam optimizer with early stopping
- Evaluation: 5-fold cross-validation with held-out test sets
Code & Reproducibility

Open Source Implementation
- Complete codebase available on GitHub
- Reproducible experiments with detailed documentation
- Pre-trained models for immediate deployment
- Comprehensive evaluation scripts for benchmark comparisons
This research was conducted at Tuskegee University’s ECE Department with support from the National Science Foundation and DoD OUSD (R&E) under Cooperative Agreement PHY-2229929 (The NSF AI Institute for Artificial and Natural Intelligence). This work represents a significant breakthrough in SAR target recognition and establishes new paradigms for self-supervised learning in radar applications.
Research Impact
This framework not only advances the state of SAR target recognition but also establishes a foundation for leveraging self-supervised learning in other domain-specific applications with limited labeled data, opening new research avenues in radar-based computer vision and autonomous systems.